Computer CPU vs GPU: What’s the Difference?
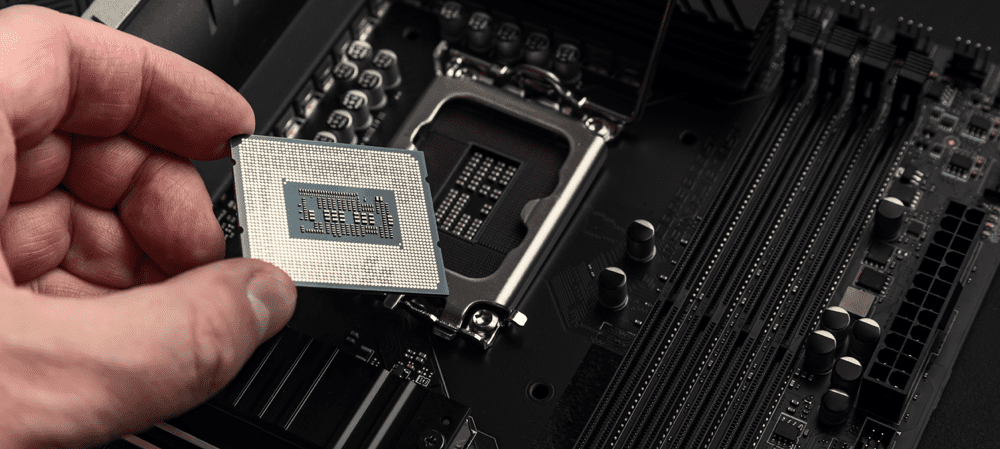
Your PC may come with two types of processors: a CPU and a GPU. What’s the difference? This guide will explain what you need to know.
There are a number of vital components inside any computer, from the RAM to the data storage. Two of the most important components, however, are the CPU and the GPU. Both will have a significant impact on the performance of your computer.
What do these two components do, and what are the differences between a CPU vs GPU? We’ll take a closer look at these two processing units at the heart of your computer below.
What is a CPU?
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit. It is often considered to be the brain of your computer.
The CPU is in charge of doing most of the work of running your computer. It does this by performing instructions sent to it from the software. For example, if you use the calculator app on your computer to add two numbers, the calculator software will send instructions to the CPU to add the two numbers together.
The CPU does this and returns the answer to the calculator app so that it can display it.
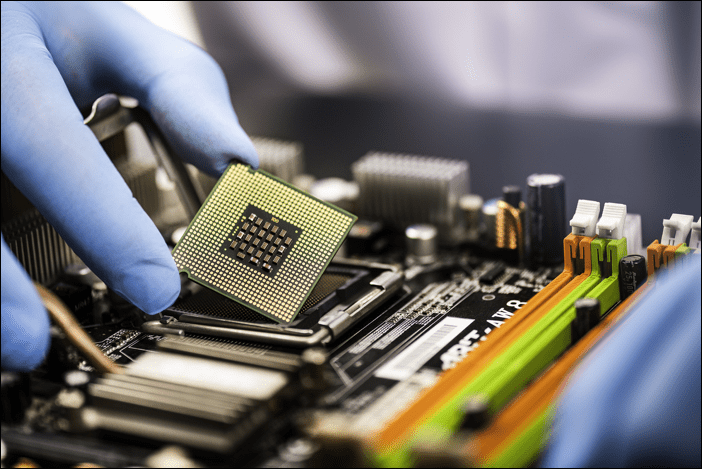

What is a GPU?
GPU stands for Graphics Processing Unit. A GPU is similar to a CPU in that its main task is to perform calculations and process instructions. Where a CPU is a jack-of-all-trades, however, a GPU is mostly focused on doing the number-crunching tasks involved in displaying graphics.
If you’re playing a video game with high-resolution 3D graphics, your CPU wouldn’t be able to handle this by itself. The GPU takes on the graphics processing so that the CPU can get on with the rest of its work. A GPU is also used for other graphics-related apps like video rendering and image post-processing.

How Does a CPU Work?
A CPU follows three basic steps. These are Fetch, Decode, and Execute.
In the first instance, the CPU fetches the next instruction it needs to perform from a specific location in your computer’s memory. It then decodes this instruction and turns it into signals that the CPU can carry out. In the final step, the CPU executes the instruction. The CPU will then move on to the next instruction, and the process repeats.
A CPU can’t perform the next instruction until the prior one is complete—it can only work on one instruction at a time. That’s why modern CPUs have multiple cores. In effect, these are multiple CPUs on a single chip. Each core is able to work on an instruction simultaneously, significantly speeding up the process.
How Does a GPU Work?
A GPU has a lot of jobs to do in a short space of time. For example, a car in a racing game can be made up of half a million polygons, each of which needs to be drawn for each frame. If the GPU had to draw all of these polygons one after another, the game would soon grind to a halt.
GPUs get around this problem by having a large number of cores. Modern CPUs often have eight or sixteen cores, but even low-end graphics cards have hundreds of cores, with high-end GPUs having more than 10,000.
These cores aren’t as fast or as capable as the cores in a CPU, but what they lack in grunt they make up for in sheer numbers. Each core can process an instruction independently. If your GPU has 10,000 cores, it can process 10,000 instructions at the same time.
What Does a CPU Do Well?
As we mentioned earlier, a CPU is a jack-of-all-trades. One of the strong suits of a CPU is its flexibility. A CPU can perform a wide range of different instructions, whereas some cores in a GPU can only perform a limited range of calculations.
CPUs also run at faster clock speeds. In essence, the rate at which they can perform calculations is faster. That makes them ideal for processes such as serial computing or running a database. The versatility of the CPU means that the vast majority of the processes that run day-to-day on your computer will go through the CPU.
What Does a GPU Do Well?
As you would expect, the GPU is very good at making the time-sensitive calculations required to render high-resolution 3D graphics at the frame rates required for smooth gameplay. This isn’t a GPUs only strong suit, however. There are other tasks that is perfect for the parallel-processing power of the GPU.
Machine learning is one area where GPUs excel. Parallel processing, where multiple instructions are carried out at the same time, is necessary to handle the vast numbers of parameters that are involved in even the simplest neural networks.
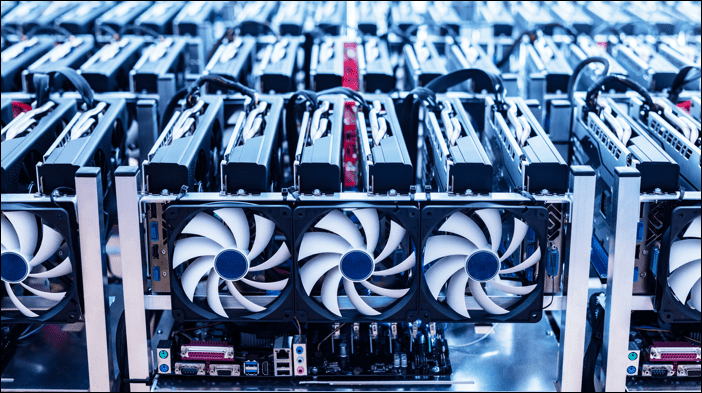
Perhaps the most notorious use of GPUs is in crypto mining. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin require processing power to verify transactions. Miners compete to complete complex calculations that are used in this verification process, and those that are successful are rewarded with small amounts of cryptocurrency.
GPUs are not only more efficient but also include specialized logic units that are ideal for solving these mathematical problems.

CPU vs GPU: Which Is Best?
With any luck, this comparison of the differences between a CPU vs GPU has given you a better understanding of these vital components of your computer. When you’re looking for a new computer, both the CPU and GPU will have a big impact on the performance.
If you’re planning on using your computer for gaming, then a powerful GPU will be key. However, if you’re only interested in casual web browsing, you shouldn’t need to go all out for the best GPU on the market.
One issue with powerful CPUs and GPUs is that they can use a lot of power and generate a lot of heat. You can monitor the CPU temperature if you’re worried that your PC is running too hot. You’ll usually be able to tell it is working too hard if your CPU fan starts running constantly. You can also keep track of your GPU performance to see if it’s holding up when gaming.
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
